HANDWRITING
Pre-Writing Skills
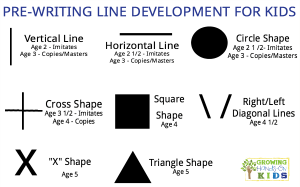
Pre-Writing Skills need to be developed before any letter formation or other handwriting skills are mastered. Pre-writing skills are the lines and strokes children from 12 months of age make using a crayon. Each of these scribbles/lines/strokes are typically developed in a specific sequence.
This developmental sequence is:
* Vertical Line – (Age 2 imitates, age 3 copies/masters)
* Horizontal Line – (Age 2 1/2 imitates, age 3 copies/masters)
* Circle Shape – (Age 2 1/2 imitates, 3 copies/masters)
* Cross Shape (+) – (Age 3 1/2 imitates, age 4 copies)
* Square Shape – (Age 4)
* Right/Left Diagonal Line – (Age 4 1/2)
* X Shape – (Age 5)
* Triangle (Age 5)
| Skill | Description | Example | Therapeutic Activities | Photo/Video |
| Visual Perceptual Skills: Visual memory | The ability to remember what was just seen. Visual memory affects the following areas of handwriting:
-the ability to write letters and words from memory |
A kindergarten student is able to write his first name on his paper without looking at his name card for the first time. | -Ask the child to look at his or her name card and then cover it up. Tell the child to write his or her name without looking. -Write a letter in sand or shaving cream, then quickly erase it and have the child write the same letter. -Give a child picture analogies for common words, such as the word “bed” looks like a bed. |
A vision therapist demonstrates visual memory activities for children and explains how they help improve functional skills. |
| Visual Perceptual Skills: Visual discrimination | The ability to distinguish similarities and differences between two objects. This skill applies to the ability to notice differences in letters with similar appearances during handwriting, such as a and o, b and d, p and q. | A first grade student writes the letters “a” and “o” using the same pencil patterns and must go back to add the stick on the “a” after a visual reminder. | -Talk the child through the formation of similar letters using verbal cues such as “Over, around, up and down” or “make magic c, then turn it into an a”* -Use puzzles, vertical writing, and multisensory writing methods to reinforce correct letter formation to emphasize the differences between similar letters. |
A vision therapist demonstrates a visual discrimination activity and explains how it helps improve functional skills. |
| Visual Perceptual Skills: Visual spatial orientation | The ability to tell the orientation and placement of objects in relation to each other. For handwriting, this skill applies to letter case, size, spacing, and placement on the writing line. For older students, it also applies to organizing a written assignment on the page. | A second grade student uses his finger to make spaces between words as he writes a sentence. | -Use darkened writing lines, highlighted writing paper, or raised line paper to give children multiple methods of input regarding line placement.
-Make a “spaceman” spacer from a small, craft size clothespin (draw a face on the top) and have a student place the spaceman between words to make the spaces. A finger or a plastic spacer also works. |
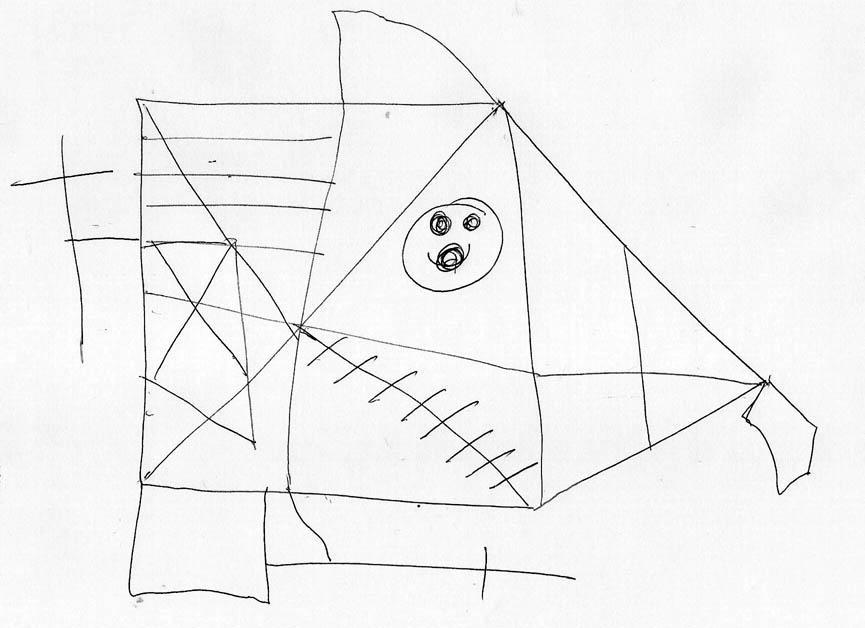
Example of the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure, used to test visual spatial orientation and visual memory. |
| Visual Perceptual Skills: Figure-ground | The ability to distinguish an object against a background. This skill relates to the ability to copy using handwriting from a board or another piece of paper without missing letters or words. | A classroom teacher writes the instructions for a science project on the classroom white board, using a different color for each step to make the instructions stand out. | -Make “word art” projects such as stencil painting a student’s name or writing words using scratch art. -Have students play hidden picture games, finding words instead of pictures. |

The game “I Spy” is based on the skill of figure-ground discrimination. |
| Ocular-Motor Skills: Saccades | The ability to move the eyes in a synchronized and precise fashion between two visual points. During handwriting, this skill is used when changing lines or paragraphs, as well as during copying from a far point. | A high school student is unable to keep up with note taking during a teacher’s lesson as she is not able to switch her gaze quickly and the teacher is switching note slides at a fast pace. | -Play trail making games on a large board and on paper.
-Play fast moving games such as ping pong or badminton. |
A man demonstrates how saccades affect eye movements during reading. |
| Visual Motor Skills | The ability to coordinate the eyes and the hands to execute precise movements. During handwriting, this skill is used to sequence pencil strokes for pre-writing figures and correct letter formation, as well as for motor control to produce correct letter size, alignment and spacing. | A first grade student with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) loses focus while writing a sentence, causing his letters to slope off the writing line. | -Use large motor movements to draw letters with correct formation in the air. -Practice letter formation by writing letters vertically on a white board, Smart board, chalkboard or easel. |
 |
| Gross Motor Skills: Proximal Stability | The ability to maintain the correct posture and arm position during handwriting.
-core strength refers to the strength and control of the trunk muscles to maintain sitting balance |
A kindergarten student with cerebral palsy and resulting poor core strength lies prone on elbows to practice writing the letters of her name. | -Using an NDT treatment approach, have a student move to a more stable posture while writing, such as prone on elbows or all fours.
-Enhance core strength by having a student sit on a t-stool or ball chair to facilitate co-contraction of the trunk muscles. |
 |
| Fine Motor Skills: In-hand manipulation skills | The ability to move and position the pencil in the hand for writing.
-translation – using the fingers to position the pencil for writing. |
A four-year-old kindergarten student must use his other hand to help adjust the pencil in his writing hand prior to drawing a picture. | -Play pencil manipulation games where a student is required to move, roll and rotate a pencil using only the writing hand. -Isolate the thumb, index and middle fingers to practice manipulation skills by having the student hold an object against his or her palm with the ring and little fingers. |
A woman demonstrates in-hand manipulation skills. |
| Fine Motor Skills: Fine motor coordination | During handwriting, fine motor coordination affects a student’s pencil grasp, as well as the ability to move the fingers in a dynamic fashion while stabilizing the wrist and forearm. This affects the student’s writing precision and speed. | A kindergarten student writes very slowly, clamping his fingers on the pencil and moving his wrist and forearm as a unit while writing his name. | -Use a visual model and verbal cues to correct a student’s pencil grasp.
-Issue an appropriate pencil grip to students who experience difficulty adjusting pencil grasp. |
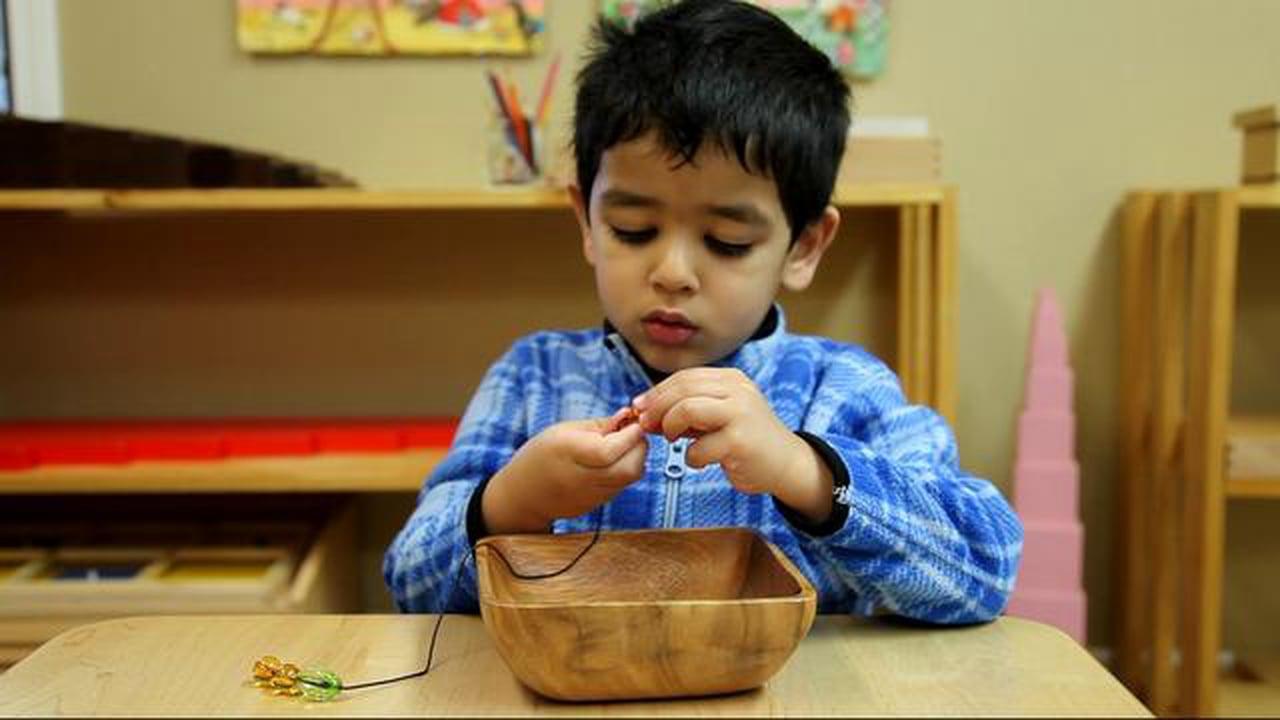 |
| Fine Motor Skills: Fine motor control | This skill affects a student’s ability to write with precision, controlling for letter size and neatness. | A 4th grade student shows improvement in the neatness of her written assignments after 2 months of occupational therapy sessions. | -Have students practice tracing letters slowly, paying attention to precision.
-Use writing apps such as Letter School or i Write Words for tablets to practice letter formation. Make sure student use a stylus to practice with a tablet app. |
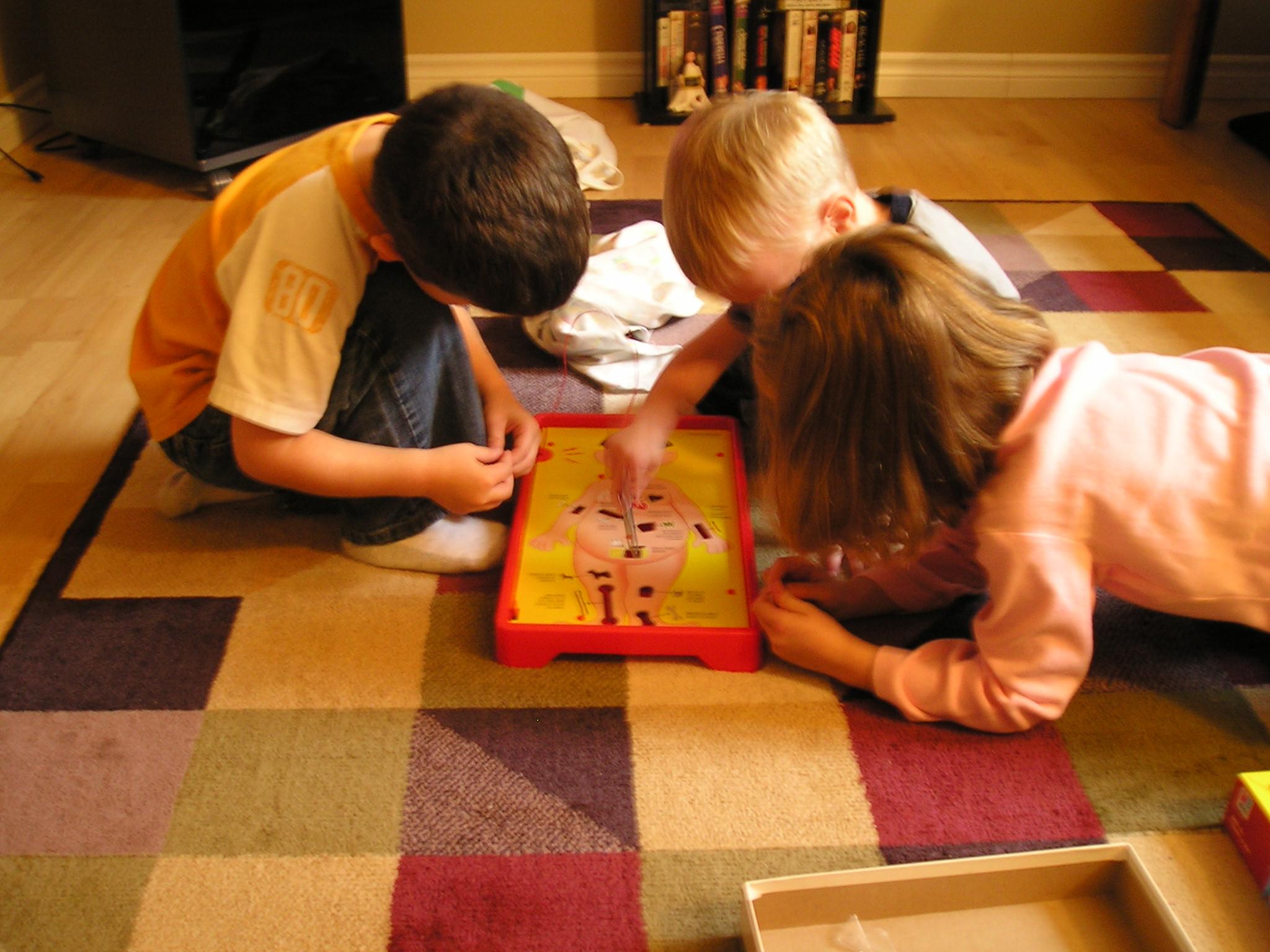 |
| Bilateral Motor Coordination | The ability to coordinate the use of two hands together to complete a task. During handwriting, bilateral motor coordination is used when one hand completes the act of writing while the other hand stabilizes the paper. | A student with a traumatic brain injury learns to use his affected hand as a “helper hand” to stabilize the paper as he writes his name. | -Prompt students to “hold the paper” with the non-dominant hand during writing. -Place the writing paper on a clipboard or a vertical surface and have the student use the non-dominant hand to stabilize the paper while writing. |
 |
| Praxis – also called Motor Planning | The ability of the brain to plan an action and then send signals to the body to carry out that action. During writing, the brain must tell the hand and fingers how to move to execute the movements involved in writing correctly.
-Crucial when children are first learning to write, as praxis is needed to execute unfamiliar movements. |
A third grade student with a learning disability forms all of her letters from the bottom up. | -Use verbal cues that provide a concrete picture, such as “line down, frog jumps up”*
-Sing songs and play body games related to letter position, such as “Where do you start your letters, at the top!”* |
Directions are given for a homemade game activity that addresses motor planning skills. A child demonstrates the game. |
| Sensory Integration: Tactile processing | The ability to tolerate the presence of and feel the shape and position of objects in the hand.
-Tactile defensiveness – sensitivity to touch in the hand. This may affect a student’s ability to hold a pencil comfortably. |
A first grade student with tactile defensiveness uses a large, squishy pencil grip when writing to make the pencil more comfortable to hold. | -Use manipulatives to form letters, such as blocks, sticks, or small objects.
-Have students make letters out of play-doh by making “snakes” and forming them into letters. |
 |
| Sensory Integration: Proprioceptive processing, also called kinesthesia. | The ability to sense the body’s position in relation to itself, which parts of the body are moving, and the amount of force exerted during movement. During writing, proprioception affects the ability to form and efficient grasp pattern, exert appropriate force on the pencil, and write in a line when a writing line is not present. Proprioception also affects fluidity of movement, information about directionality, sitting posture, joint stability, and handwriting speed. -Research shows that students who have poor proprioception rely in visual input for writing, slowing the writing process.^ |
A third grade student uses small weights on his pencil to help him hold the pencil in the correct position while writing. | -Complete activities while seated on a therapy ball to help improve posture and core stability.
-Play catch with a weighted ball to provide proprioceptive input to the arms and hands. |
Children demonstrate how problems with the proprioceptive system affect function. |
| Sensory Integration: Vestibular processing | The ability to sense the body’s position in relation to its surroundings, including the ability to sense and tolerate movement.
-affects sitting posture and the ability to know when posture is correct – helps to prevent leaning on the desk, table, or other students. |
A first grade student sits on a ball chair to improve posture during handwriting. (Research supports sitting on a ball to improve handwriting ^^.) | -Complete visual motor activities while lying prone on a swing, scooter board, or therapy ball to reinforce visual motor skills in different postural positions.
-Complete vertical handwriting or visual motor drawing tasks while standing on a balance board. |
Children demonstrate how problems with the vestibular system affect function. |
*from the Handwriting Without Tears program by Jan Olsen, OT
^Tseng, M.H. and Chow, S.M.K. (2000). Perceptual-motor function of school-age children with slow handwriting speed. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 54, 83-88.