The terms “bottom-up” and “top-down” refer to the approach occupational therapists take when evaluating and treating patients.
Definitions
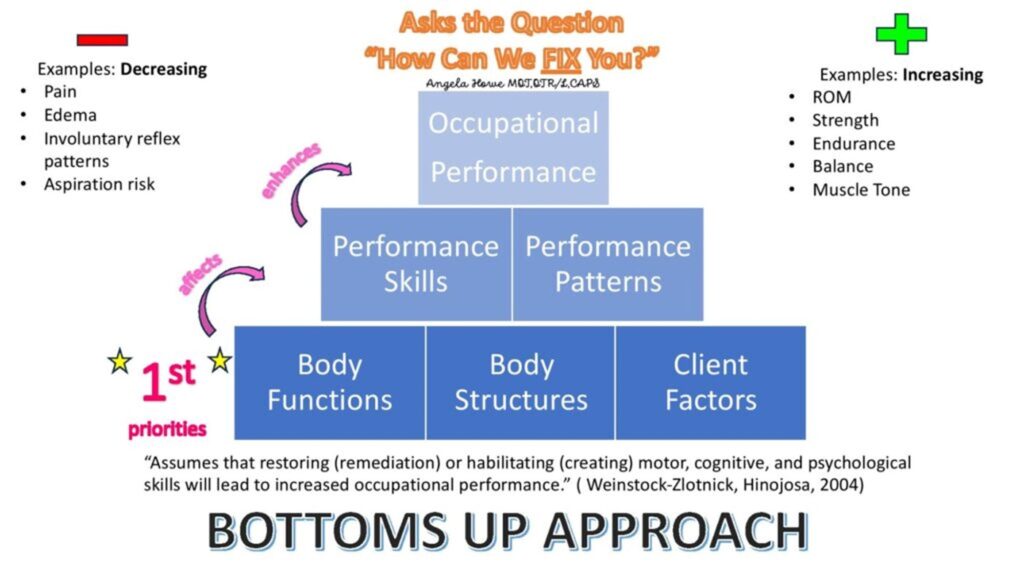
Bottom-Up Approach: The occupational therapist evaluates the foundational components of function and develops the treatment plan based on deficits in these components.
Comparison: Bottom-Up Approach vs Top-Down Approach
This chart will focus on the definitions and differences between these two approaches.
| Bottom-Up Approach | Top-Down Approach | |
| Therapeutic Method | Restorative | Compensatory |
| Desired Outcome | To acquire or restore the skills necessary to participate in occupation. | To maximize existing skills and adapt activities to allow independence in occupation. |
| Focus | Focuses on the cause of deficits in foundational skills. The evaluation and treatment plan is designed to address deficits in foundational skills, allowing for increased performance during daily activities. | Focuses on the skills necessary to participate in daily activities. The evaluation and treatment plan is designed to address participation in activity, including adaptations required to allow participation. |
| Approach to Intervention | Addresses the cause of the problem. Treatment goals address the level of impairment and aim to improve functional skills. | Addresses functional performance. Treatment goals address participation in functional activity at the existing level of disability. |
| Frames of Reference Examples | -Biomechanical -Neurodevelopmental Treatment (NDT) -Sensory Integration -Brunnstrom Movement Therapy -Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) |
-Allen Cognitive Levels -Canadian Model of Occupational Performance -Model of Human Occupation (MOHO) -Occupational Adaptation |
| Advantages | -Easy to apply to all patients, even those who cannot communicate or make decisions for themselves. -Fits in well with the biomedical approach used in most hospitals and clinics. -Easy to collect and track data for outcomes analysis. -Allows for time sensitive intervention (i.e. prompt treatment of burns, splinting after tendon graft). |
-Consistent with the principles on which occupational therapy was founded as a profession. -Allows for a holistic approach. -Allows for intervention with patients who display occupational limitations but not necessarily the medical diagnoses that might underlie limitations (i.e. school based therapy). |
| Disadvantages | –Utilizes frames of references and theories from other professions. -Objective is to improve function, not necessarily to attain independence during occupation. |
-Assessments used are not always objective. -Models are not always readily applicable to treatment settings. (Lots of theory, not a lot of treatment examples or practical treatment tools.) |
Bottom-Up Approach
Examples – Bottom-Up Approach
| Evaluations | Treatment Techniques | Photo |
| Goniometer measurements
Dynamometer and pinch meter measurements Manual muscle test Nine-hole peg test Purdue Pegboard test Ocular motor tests Motor-Free Visual Perception Test Peabody Developmental Motor Scales Sensory Profile |
Passive range of motion techniques -passive stretching -splinting -positioning . Active range of motion activities -reaching for cones -dowel exercises -range of motion arc .. Strengthening exercises -wrist weights -pulleys -Theraputty -clothespins . Fine motor activities -pegboard designs -lacing -sorting small objects . Visual motor/perceptual activities -video games -parquetry -puzzles -word search . Sensory integration activities -swinging -scooter board games -play in balls or foam blocks -brushing program |

|
Summary of Bottom-Up Approach
Top-Down Approach
Examples – Top-Down Approach
| Evaluations | Treatment Techniques | Photo |
| Activities of Daily Living Checklist/Observation
Home assessment Kohlman Evaluation of Living Skills Independent Living Scales School Function Assessment Functional Capacity Evaluation/Workplace Assessment |
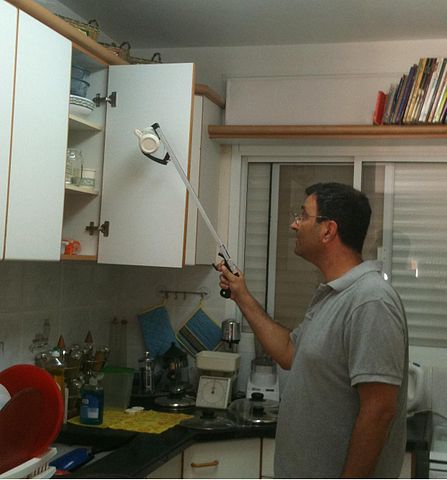
Instruction in adaptive techniques -one handed dressing -energy conservation -joint protection -sliding transfers . Provision of and instruction in use of adaptive equipment -reacher -sock aid -one handed can opener -tub bench . Provision of and instruction in use of assistive technology -environmental control center -ergonomic keyboard -speech to text typing -talking calculator . Adaptations to the environment -wheelchair ramp -grab rails -adjustable seating at work station -lift chair -adjustable bed -standing desk |

|
Summary of Top-Down Approach
