Physical Agent Modalities
Physical agent modalities are those procedures and interventions that are systematically applied to modify specific client factors when neurological, musculoskeletal, or skin conditions are present that may be limiting occupational performance. PAMs use various forms of energy to modulate pain, modify tissue healing, increase tissue extensibility, modify skin and scar tissue and decrease edema/inflammation. PAMs are used in preparation for or concurrently with purposeful and occupation-based activities. PAMs may only be applied by OT’s and OTA’s who who have documented evidence of possessing the theoretical background and technical skills for safe and competent integration of the modality into the occupational therapy plan.
| Physical Agent Modality | Description | Indications | Administration Techniques | Precautions/Contraindications | Image |
| Cyrotherapy/Cold pack | Cold | Used for pain management, anti inflammation, edema control, decrease of muscle guarding, spasm.
-Cold therapy should be the modality of choice in the acute state following trauma. Cold may be uncomfortable at first but pain, edema, inflammation and muscle spasm will ultimately be reduced. -Cold is often used in conjunction with rest compression and elevation.a. RICE – Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation -Cold in combination with static stretch or contract relax technique has been recommended for reducing muscle spasm or decreasing exercise induced muscle soreness thus increasing ROM. |
Cooling agents include:Cold packs, ice massage, cold baths, vapocoolant spray, cold gel, controlled cold compression units | Cautiously used on patients with sensory deficits, circulatory impairment, cold hypersensitivity, hypertension.-Cryoglobulinemia is a disorder characterized by the presence of an abnormal blood protein that forms a gel when exposed to low temps. This gel formation can lead to ischemia or gangrene.
-Raynaud’s phenomenon is a vasospastic (a sudden constriction of a blood vessel that reduces blood flow) disorder that is idiopathic (a disease that has no known cause) or associated with other disorders. Cycles of pallor, cyanosis,rubor, numbness, tingling or burning.
|
 |
| Heat (Paraffin Bath, Hot Packs, Fluidotherapy) | PAM must benefit tx. Used as adjunctive intervention in preparation for purposeful, functional activity. | Relieves pain , increases soft tissue extensibility , assists in wound healing | No heat for cancer, blood clots. |  |
|
| Fluidotherapy | Superficial heating modality that transfers heat by convection. Dried corn husks or other cellulose material are suspended by warmed circulating air | Mainly used to help patients with their hands and wrists or for patients with arthritis, chronic tendonitis, postoperative conditions, postfracture management, and Raynaud’s syndrome (The fingers, toes, ears, and tip of the nose, feel numb and cool in response to cold temperatures or stress. It’s often accompanied by changes in the color of the skin). | The machine is heated to desired temperature, then the distal limb is placed inside the fluidotherapy cabinet. Turbulance of the suspended particles can be controlled. Treatment time is typically 15-20 minutes. | Cautiosly used in the presence of open wounds. Open wounds must be covered with a plastic barrier to prevent cellulose particles from entering the wound. | |
| Interferential Current (IFC) | IFC uses two wave kilohhertz frequencies and creates an interference between them, resulting in a unique current | Used for pain management, edema reduction, and muscle spasm reduction. | Uses four electrodes set up so that the two wave currents intersect one another perpendicularly. Intensity is increased to patients tolerance. Patients should feel a comfortable tingling sensation. | Electrodes should not intersect thoracic cavity. Contraindicated during pregnancy, in the presence of a cardiac pacemaker, or other implanted electrical simulators. Precautions include obesity, impaired sensation, over superficial implants, and impaired cognitive abilities. | 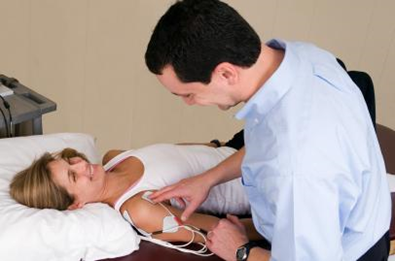 |
| Iontophoresis | A continuous direct current used to transmit ions through the skin. | Used for pain management, anti inflammation, scar lysis, and enhanced healing | Uses two electrodes; one active and one dispersive. Best applied to a specific, localized, and relatively superficial target tissue. Such tendons include the rotator cuff tendons, common wrist/finger/hand flexor and extensor origins. | Contraindicated in areas with bruises, cuts, broken skin, acute injuries, impaired sensation, and over sites of active hemorrhage. | 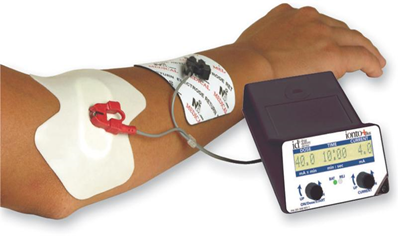 |
| Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) | Activate muscle by stimulating an intact or partially intact peripheral nerve. | Used to stimulate paralyzed, paretic muscle, muscle weakness, peripheral neuropathy, and muscle spasm. | Pulse amplitude is gradually increased within the patients sensory tolerance limits. | Contraindicated in pregnancy, cancer, presence of a cardiac pacemaker, or any other electrical simulators. Precautions include obesity, impaired sensation, and over relatively superficial metal implants. | 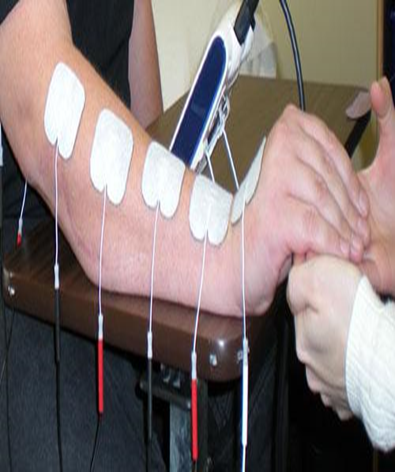 |
| Paraffin baths | Superfical heat by coating the target area with solution with melted paraffin wax and mineral oil. | Used to treat chronic arthritis of the hand, various distal extremity conditions to increase ROM, manages pain, and assists in wound healing. | Dip technique-the distal extremity is coated with 8 to 12 coats of paraffin. Then the distal extremity is wrapped in plastic and then a terry towel. The patient is positioned so the extremity is elevated. The paraffin glove remains in place for 15 to 20 minutes. | Contraindicated in the presence of an open wound. |  |
| Transcutaneous Electrial Nerve Stimulation (TENS) | Used to stimulate sensory and/or motor nerves in an effort to manage pain. | Used to treat chronic pain syndrome, spinal radiculopathy, low back pain, reflex sympothetic dystrophy, etc. | Uses high pulse rate and low pulse width. Patients should be allowed to ambulate, perform ADL’s, and occupational tasks while the modality is administered. | Contraindicated with patients who are pregnant, have pacemakers, or are prone to getting seizures. . TENS “pulses” have the potential to trigger a seizure. | 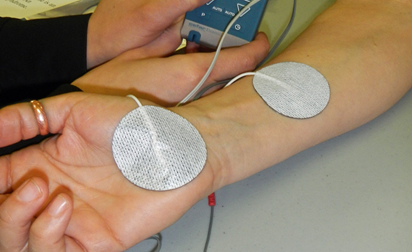 |
| Ultrasound | Deep heating modality. Sound waves are extremely low intensity and very high frequency are introduced to tissue, producing theramal and nonthermal effect. | Used to increase the extensibility of collage fibers in tendons and joint capsules, reduce muscle spasms, and modulate pain. May positively affect healing in damaged tissue by alternating the permeability of cells. | Conducting gel is required. | Contraindicated in areas of decreased circulation, impaired sensation, and pregnancy. i.e. ultrasound never used over a growth plate. While recent research shows some promise for ultrasound as an effective treatment to accelerate healing of fractures, AOTA’s official stance is that ultrasound is contraindicated for fractures. | 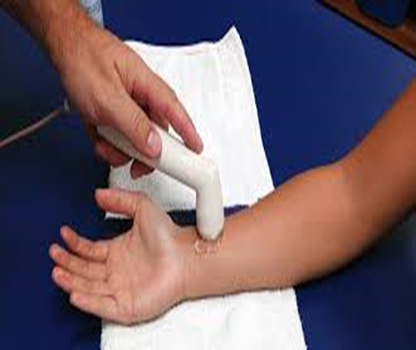 |
| Whirlpool | Cleans/debrides open infected wound. Water temperature does not reach therapeutic range to use as a heat modality. Use of a whirlpool allows dressings to be removed slowly and gently reducing the pain of dressing changes in patients with sensitive wounds such as crush injuries, venous stasis,arterial insufficiency, etc. The warmth of the water promotes increased circulation to the wound surface, and can be soothing for the patient. | Precautions/Contraindications: Cancer, pacemaker, pregnancy, cognitive, sensory OR vascular impairment |  |
||
| Contrast baths | Hot/cold immersion therapy is a method of treating muscle soreness, swelling, and inflammation. It is also used for treating joint injuries, mild sprains, symptoms of chronic pain and repetitive strain injuries. | Used to reduce edema |  |
Think you’re ready for the NBCOT® Exam?
See where you stand instantly by taking our 5 minute practice test