Mental Health Diagnoses and Behaviors (PART – 1)
People with mental health diagnoses often display certain patterns of behavior. The following charts will review mental health diagnoses, some of the behaviors associated with mental health conditions, and the therapeutic approaches that have been determined to be effective in addressing these behaviors.
Anger/Hostility

| Description, Symptoms, and Challenges | Associated Diagnoses | Support and Treatment | Key Elements to the Therapeutic Approach and Environment | Sample Activities | Video Example |
| An emotion that gets the body ready to fight. -Anger: strong feeling of displeasure -Hostility: unfriendly and threatening attitude directed toward others -May manifest through physical or verbal violence, stiffening, destruction. -May start with sarcasm |
-Psychotic disorder -Schizophrenia -Bipolar disorder -Psychotic depression -Organic mental disorder Some brain disorders |
Get the patient to talk Use your words instead of acting out Speak to patient individually Avoid punishing or criticizing Instruct the patient how to correct behavior Be direct and clear about what is expected |
Stay a few feet away and do not face them directly Stay out of person’s reach Stay close to the exit Keep the door open Do not treat the patient alone Remove all weapons or potential weapons No brooms or mops |
Journaling Complete a feelings worksheet Wii for boxing Collage Art projects – ripping magazines for pictures – have a theme for them to follow during art – projects that sequence a destructive activity followed by a constructive activity |
A woman with bipolar disorder discusses anger |
Anxiety
| Description, Symptoms, and Challenges | Associated Diagnoses | Support and Treatment | Key Elements to the Therapeutic Approach and Environment | Sample Activities | Video Example |
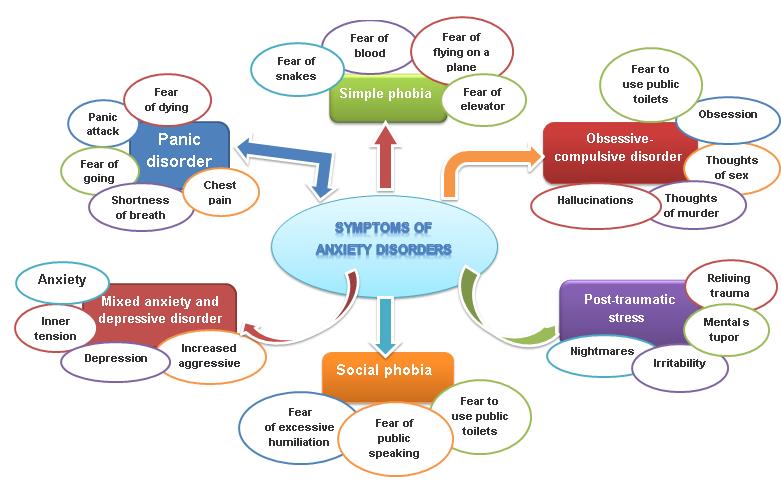
| Symptoms: Tension, nervousness, panic attacks, increased heart rate, worry, trouble sleeping, sweating, and gastrointestinal issues. A patient may feel an overwhelming sense of dread, an intense fear of death, injury, or “bad things happening”. State of tension and uneasiness that the ego is unable to resolve-Most people can control anxiety but some people cannot -Difficulty balancing fear reactions with reality-based thinking -Fear reactions may be out of proportion with the situation -Medication may be prescribed to manage anxiety |
Found in almost every diagnosis -Commonly occurs in people with depression, OCD, autism, ADHD, bipolar disorder -Psychopaths and sociopaths do not experience anxiety |
Talk therapy is commonly used to treat anxiety. Often if a patient can get to the root cause of their anxiety they can overcome it. Medication to manage anxiety can also be prescribed. Anxiety and Anxiety Disorders can also result from other, underlying medical conditions and often need to be addressed from multiple angles. Alternative therapies such as yoga, meditation or prayer, chiropractic care, and diet and lifestyle changes are also effective in treating anxiety. | Allow the person to express himself or herself and help him or her to learn to do it if he or she cannot. Concentrate on productive activities. Listen to the person’s fears. Redirect the person’s attention to a neutral topic Be flexible in the response to the person’s anxiety – everyone reacts differently.-Ritualistic response: never criticize -Phobic response: encourage patients to talk about fears -Intrusive: reassure you will be available Keep the therapy environment calm and comfortable. Schedule therapy at a time when the clinic is not crowded. Give the person a tour of the therapy clinic. Provide the person with a schedule of planned therapeutic activities. Help the person feel secure |
Yoga Progressive relaxation Journaling with structure- helps to see antecedents Just right challenge Simple cooking tasks Guide patients to choose activities Education in diet and lifestyle changes |
A television news anchor talks about the panic attack he had on television. An entertaining lecture about anxiety disorders. |
Borderline Personality Disorder

| Description, Symptoms, and Challenges | Associated Diagnoses | Support and Treatment | Key Elements to the Therapeutic Approach and Environment | Sample Activities | Video Example |
| Symptoms: -Destructive, dangerous, hostile or harmful behaviors. -Suicidal thoughts and depression -An overstated focus on self, self absorption, conceit -Difficulty building and maintaining relationships -General emotional instability -Mood swingsThis is a broad disorder and can be hard to diagnose and treat. Patients are unstable and standard treatment often requires hospitalization |
Mood disorders
Anxiety disorders Eating disorders Substance abuse |
Talk therapy, anger management techniques and medication are all common treatments for Borderline Personality Disorder. | The OT should make all attempts to help the patient to feel connected and included. Patients with BPD suffer from feelings of abandonment and isolation so any changes in care or setting may be unsettling. Moods can change quickly so be alert and know the signs and symptoms | -Group activities and games
-Crafts and hobbies, especially familiar tasks that the patient can complete successfully -Cooking and education in nutritional food preparation -Relaxation techniques, yoga |
A celebrity rehabilitation doctor discusses borderline personality disorder |