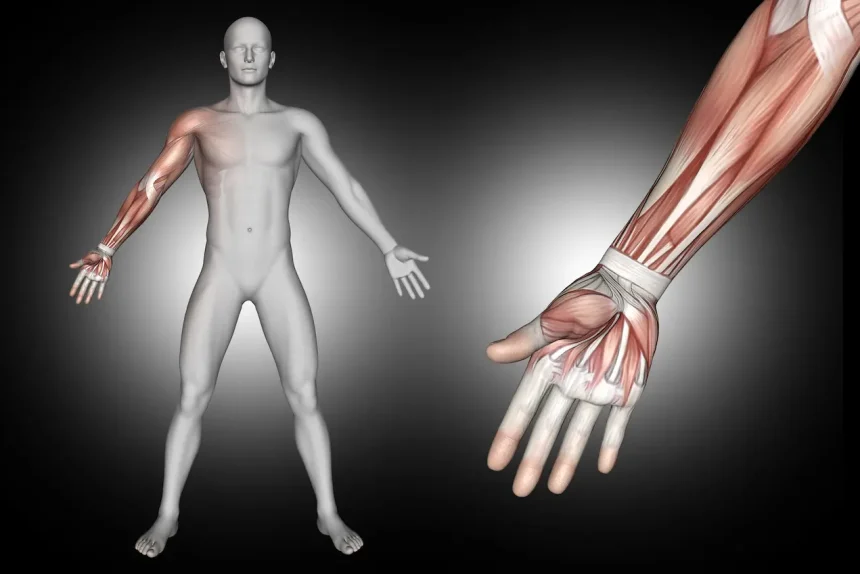
Understanding the Joints and Nerves Distribution
Mastering the knowledge of joint structures and nerve pathways is crucial for tackling the NBCOT® exam. Understanding the following key elements will strengthen your foundation:
- Focus on the distribution of nerves throughout the arm, including distinctions between median, ulnar, and radial nerve pathways.
- In our full guide, we break down each developmental group with detailed case examples.
Static Thenar Web Spacer Splint
Use of static thenar web spacer splint is essential in managing conditions like “ape hand deformity.” This splint helps maintain correct thumb positioning, crucial for patients with median nerve injuries.
Explore the full guide for a comprehensive review of dynamic and static splint types.
Flail Arm Splint: Efficacy in Brachial Plexus Injury
For conditions like brachial plexus injury, a flail arm splint provides stability. It prevents joint over-extension and facilitates functional arm positioning.
Interactive case scenarios in our member area demonstrate splint applications.
Ape Hand Deformity: Identification and Management
The ape hand deformity, often stemming from severe median nerve damage, results in impaired thumb opposition. Understanding visual and physical assessment techniques is vital for effective management.
Ape Hand Splint Techniques
Besides static thenar web spacer splint, several other techniques support patients with ape hand deformity. Precision in customizing splints can significantly expedite recovery.
In our detailed guides, learn through quizzes and case studies to recognize this deformity.
Contents of Carpal Tunnel Mnemonic
Recall the carpal tunnel contents with ease: “Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle”—a mnemonic to remember Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, and Hamate.
Tactics for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Management
Ideal positioning and ergonomic interventions are key in reducing carpal tunnel symptoms. Mastering wrist splint applications enhances occupational therapy outcomes.
Test your application skills with our exclusive practice exams.
Ulnar Nerve Dermatome: Key Clinical Insights
The ulnar nerve dermatome impacts sensory distribution predominantly along the little finger and ulnar half of the ring finger. Knowing this assists in diagnosing nerve compression syndromes.
Our detailed course content includes interactive maps to deepen understanding.
Want detailed practice tips to ace the NBCOT® exam? Join now for full access!
What is the significance of understanding nerve distribution for the NBCOT® exam?
Understanding the distribution of nerves, including median, ulnar, and radial nerve pathways, is essential for tackling questions on joint structures and nerve pathways in the NBCOT® exam, enhancing diagnostic and therapeutic skills.
How does a static thenar web spacer splint help with ape hand deformity?
A static thenar web spacer splint helps manage ape hand deformity by maintaining the correct thumb position, crucial for patients suffering from median nerve injuries. It aids in preventing further deformity and improving hand functionality.
What role does a flail arm splint play in brachial plexus injury management?
A flail arm splint provides stability and prevents joint over-extension in brachial plexus injuries, facilitating functional arm positioning and enhancing rehabilitation outcomes.
How can I memorize the contents of the carpal tunnel easily?
Use the mnemonic “Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle” to easily recall the carpal tunnel’s contents: Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, and Hamate.
What sensory distribution is associated with the ulnar nerve dermatome?
The ulnar nerve dermatome predominantly affects the sensory distribution along the little finger and the ulnar half of the ring finger, helping in diagnosing nerve compression syndromes.