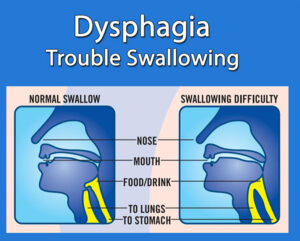
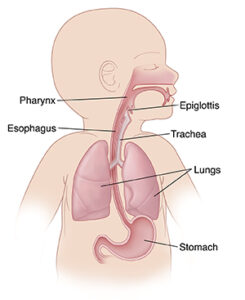
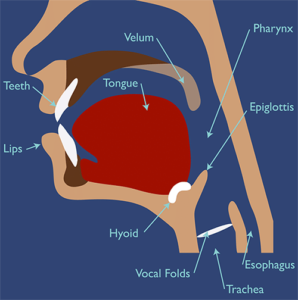
Dysphagia is a swallowing disorder impacting nutritional intake and airway protection. Essential for NBCOT® candidates, understanding its treatment goals is crucial. Explore phases of swallowing—oral, pharyngeal, and esophageal—and identify signs of dysphagia like aspiration pneumonia, weight loss, and sialorrhea. Mastery of this topic is vital for the NBCOT® exam.
Tonic Bite Reflex in Occupational Therapy
Handling the tonic bite reflex is key for therapists. This reflex is an involuntary jaw closure causing feeding challenges. Implement strategies such as using a coated flat spoon and maintaining a calm environment. Never forcefully remove utensils from the mouth. Understanding these techniques is critical for comprehensive patient care in occupational therapy.
Identifying Difficulty Swallowing Saliva
Spotting signs of difficulty swallowing, particularly saliva, can save lives. Symptoms include coughing during meals and a wet-sounding voice. Educating patients on these indicators and the significance of upright posture post-eating reduces aspiration risks. Video fluoroscopy is often used for diagnosis where oral exams fall short. Can you outline the steps you would take in identifying swallowing difficulties?
Bite Reflex in Adults & Pediatrics
The bite reflex isn’t just a pediatric concern. Adults may also exhibit this reflex, affecting swallowing and nutritional intake. Recognize its signs, utilize adaptive utensils like angled spoons, and employ positioning techniques for effective intervention. Ask patients to describe their symptoms during swallowing assessments for better insights.
Feeding Strategies for Cerebral Palsy (CP)
Feeding children with CP requires tailored strategies. Consideration of food type and utensil choices, along with posture alignment, promotes safe swallowing. Diet modifications and pacing support safe food intake. Explore personal case studies to see real-world applications of these methods. What postural techniques can you use to support CP patients during meals?
Approaches to Managing Dysphagia Diets
The Dysphagia Diet framework ranks foods and liquids from 0-7 for safe swallowing. It’s vital for NBCOT® exam prep. Levels range from thin liquids to mixed textures. Focus on practical applications—practice preparing pureed meals and recognize the importance of avoiding chunky foods. Can you list foods suitable for each level of the dysphagia diet?
Occupational Therapy Swallowing Intervention
Swallow therapies integrate positioning technology and adaptive tools, ensuring effective swallowing. Recognize how to incorporate chin-tuck and head rotation techniques. Each therapeutic choice must be personalized, and understanding these strategies is non-negotiable for future occupational therapy professionals. How might these interventions vary for different patient needs?
Want detailed practice tips to ace the NBCOT® exam? Join now for full access!
What are the primary signs of dysphagia?
Primary signs of dysphagia include aspiration pneumonia, weight loss, sialorrhea, coughing during meals, and a wet-sounding voice. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for effective intervention and prevention.
How can occupational therapy address the tonic bite reflex?
To manage a tonic bite reflex, therapists can use a coated flat spoon, implement a calm feeding environment, and avoid forcibly removing utensils. These strategies help reduce feeding challenges associated with this reflex.
What postural techniques support safe swallowing in CP patients?
Supporting CP patients during meals involves aligning posture, possibly using adaptive seating to ensure stability and alignment, and pacing food intake to promote safe swallowing. Tailoring these strategies to individual needs is essential.
Can adults exhibit a bite reflex, and how is it managed?
Yes, adults can exhibit a bite reflex affecting swallowing. Management includes using adaptive utensils like angled spoons, positioning techniques, and asking patients to describe their symptoms for tailored interventions.
What are the different levels of the Dysphagia Diet framework?
The Dysphagia Diet framework ranks foods and liquids from level 0 to 7, catering to different swallowing abilities. Levels range from thin liquids to mixed textures, focusing on the preparation of pureed meals and avoiding chunky foods to ensure safe swallowing.



