Occupational therapists often encounter clients with traumatic backgrounds, emphasizing the importance of trauma-informed care in various settings, not limited to mental health. Understanding the multifaceted nature of trauma allows therapists to support individuals in managing their past experiences for better outcomes.
Understanding Trauma in Occupational Therapy
Trauma involves intense reactions of fear, helplessness, and loss of control due to adverse events, including violence, disasters, and abuse. Both singular and cumulative experiences can impact mental, physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being, affecting daily function.
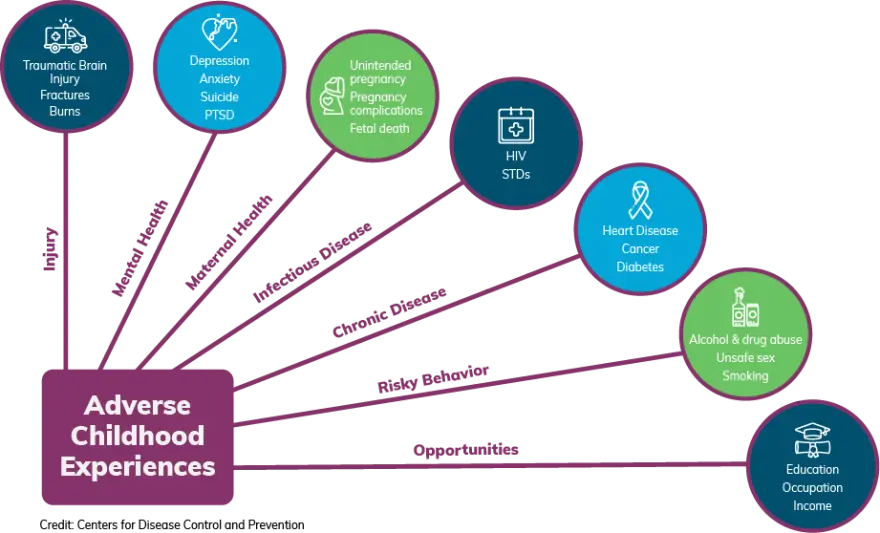
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
ACEs refer to traumatic events in childhood (ages 1-17) that can influence lifelong emotional, behavioral, and physical health, potentially leading to chronic conditions or mental health issues. Common ACEs include abuse, neglect, and family dysfunction.
The Impact of Trauma on Children’s Development
Chronic stress and trauma can keep a child’s brain in a survival mode, impacting their cognitive and emotional development, particularly the prefrontal cortex, which is crucial for attention and executive functioning. In nurturing relationships, children learn trust and self-worth, highlighting the caregiver’s role in a child’s development.
Occupational Therapy for Trauma
Practioners must evaluate the extent of trauma symptoms impacting occupational performance, including emotional regulation and social participation, and design recovery-focused interventions addressing sensory integration, coping skills, and familial relationships.
Trauma-Informed Occupational Therapy Principles
According to SAMHSA, a trauma-informed approach should recognize the impact of trauma, understand recovery paths, incorporate trauma knowledge into practices, and avoid re-traumatization. The approach is guided by principles such as safety, trustworthiness, peer support, and cultural competence.
Developing Resilience Through Occupational Therapy
Resilience is the ability to adapt to challenging experiences. ACEs can interfere with development, but interventions can help build resilience and support positive outcomes like academic achievement and social success.
Trauma Responsive Occupational Therapy in Action
Effective therapy involves asking, “What happened to you?” rather than “What’s wrong with you?” This approach encourages understanding and healing. Practitioners should use evidence-based strategies and offer training for staff to better recognize and respond to trauma.
| Do | Do Not | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Ask preferred pronouns | Assume pronouns based on appearance | Cultural, historical, and gender issues |
| Acknowledge uncontrollable environmental aspects | Ignore trauma-related needs | Safety, Trustworthiness |
Interactive Question: Can you think of other ways trauma-informed care can be incorporated into occupational therapy practice?
Want detailed practice tips to ace the NBCOT® exam? Join now for full access!
What is trauma-informed care in occupational therapy?
Trauma-informed care in occupational therapy involves recognizing the impact of trauma on a client’s life and designing therapeutic interventions that support healing and recovery. This approach emphasizes understanding trauma paths, incorporating knowledge into practice, and avoiding re-traumatization.
How does trauma affect a child’s development?
Trauma during childhood can keep a child’s brain in a survival state, affecting cognitive and emotional development. It particularly impacts the prefrontal cortex, crucial for attention and executive functioning, which can hinder a child’s learning and growth.
What are Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and why are they important?
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) are traumatic events experienced in childhood such as abuse or neglect. They are significant because they can influence lifelong health, potentially leading to chronic conditions and mental health issues if not addressed.
How can occupational therapy help build resilience in clients with a trauma history?
Occupational therapy can help build resilience by developing personalized interventions that focus on enhancing coping skills, improving emotional regulation, and strengthening familial relationships to support positive outcomes like academic achievement and social success.
What are the key principles of trauma-responsive occupational therapy?
Key principles of trauma-responsive occupational therapy include safety, trustworthiness, peer support, and cultural competence. Practitioners should also address cultural, historical, and gender issues by respecting clients’ pronouns and acknowledging trauma-related needs.