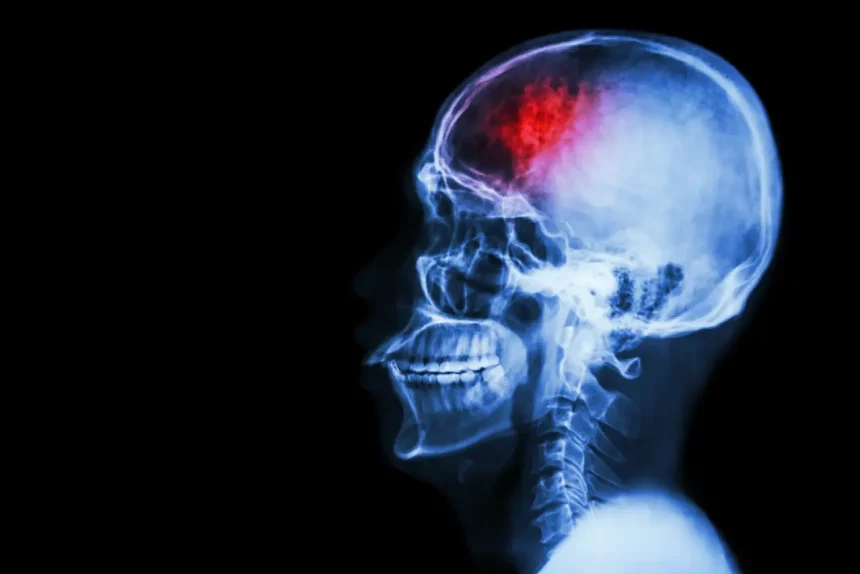
A Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a complex injury with varying symptoms and disabilities. It ranges from a brief alteration of consciousness in mild cases to prolonged unconsciousness or death in severe cases. This condition often results from the brain being harmed by a mechanical force, such as a rapid acceleration-deceleration or a direct impact.
TBI Severity Classification
Understanding TBI severity is crucial for effective treatment. The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a primary method for classifying TBI severity:
- Severe TBI: GCS score of 3-8
- Moderate TBI: GCS score of 9-12
- Mild TBI: GCS score of 13-15
In our full guide, we delve further into GCS with case examples and explain how it impacts treatment strategies.
Classification of TBI
TBIs are categorized further into primary and secondary injuries:
- Primary Injury: Occurs at the time of the trauma.
- Secondary Injury: Occurs as a result of physiological response to the initial injury.
Within these categories, TBIs can also be focal, like skull fractures, or diffuse, like diffuse axonal injury.
TBI Levels and Symptoms
The different levels of consciousness and cognitive functions after a TBI can be understood through scales like Rancho Los Amigos Scale. Symptoms vary greatly and can include:
- Vomiting
- Lethargy
- Confusion
- Paralysis
- Vision changes
- Speech difficulties
Vegetative State Symptoms
Understanding symptoms associated with states of consciousness like the vegetative state, where patients appear awake but are unaware of themselves or their environment, is essential.
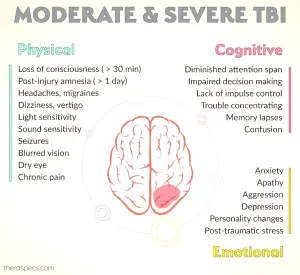
Moderate TBI Symptoms
Moderate TBIs often present symptoms such as confusion, headache, and balance issues. Effective management of these symptoms involves comprehensive rehabilitation plans.
OT Interventions for TBI
Occupational Therapy (OT) interventions play a critical role in TBI recovery:
- Motor function improvement: Rehabilitation programs focus on balance and coordination.
- Improving ADLs: Activity-based interventions tailored to individual goals.
- Enhancing self-awareness: Video feedback helps in acknowledging deficits.
- Memory strategies: Techniques like self-generation aid in better retention.
Explore more OT strategies in our comprehensive guide, which includes practical exercises and case studies.
Want detailed practice tips to ace the NBCOT® exam? Join now for full access!
What is Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) and how can it occur?
A Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is a complex injury resulting from mechanical force, such as rapid acceleration-deceleration or direct impact. Symptoms and severity can vary widely, ranging from mild cases with brief unconsciousness to severe cases with prolonged unconsciousness or death.
How is TBI severity classified and what does the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) involve?
TBI severity is classified using the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Severe TBI is indicated by a GCS score of 3-8, moderate TBI by a score of 9-12, and mild TBI by a score of 13-15. This scale helps determine the treatment strategy and prognosis for the patient.
What are the primary and secondary injuries in TBI, and how do they differ?
Primary injuries occur at the time of the trauma, while secondary injuries result from the physiological response to the initial injury. TBIs can be further characterized as either focal, like skull fractures, or diffuse, such as diffuse axonal injury.
What symptoms are associated with different TBI levels?
Symptoms of TBI can vary greatly. Common symptoms include vomiting, lethargy, confusion, paralysis, vision changes, and speech difficulties. Severity of symptoms often correlates with the TBI classification, where mild cases might show subtle cognitive changes, and severe cases may involve significant neurological dysfunction.
How can Occupational Therapy (OT) interventions aid in TBI recovery?
Occupational Therapy interventions for TBI focus on improving motor functions, aiding daily living activities (ADLs), enhancing self-awareness, and utilizing memory strategies. These interventions are tailored to individual needs and are vital in the rehabilitation process, promoting better recovery outcomes.