Overview of Parkinson’s Symptoms
Parkinson’s Disease is a progressive disorder affecting the nervous system. Its hallmark symptoms—tremor, rigidity, and voluntary movement disorders—highlight dysfunction in both voluntary and involuntary movements. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for NBCOT® exam prep.
Tremor
A resting tremor, often described as a pill-rolling tremor, is a key sign of Parkinson’s. Typically occurring at rest, it may subside with voluntary movement. However, some patients experience persistent tremors during functional activities.
Rigidity
Muscle stiffness impedes movement, presenting as cogwheel or lead pipe rigidity in PD. This rigidity, along with other symptoms, often leads to difficulties in performing activities of daily living (ADL) like eating and dressing.
Voluntary Movement Disorders
Difficulty initiating movements (akinesia) and maintaining movement speed (bradykinesia) are disabling for PD patients, affecting tasks such as driving and writing. Hand dysfunction further complicates tasks due to poor manual dexterity and coordination.
How Many Stages of Parkinson’s Are There?
The progression of Parkinson’s Disease is typically divided into five stages:
- Stage 1: Mild symptoms with minimal functional impairment.
- Stage 2: Early bilateral symptoms with facial masking and speech changes.
- Stage 3: Mid-stage with balance issues and slowness of movement.
- Stage 4: Severe symptoms, movement impairment, assistance needed for ADLs.
- Stage 5: Most advanced; requires wheelchair or bed confinement, round-the-clock care.
Signs of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms are memorized easily with the mnemonics TRAP and SMART:
- TRAP: Tremor, Rigidity, Akinesia, Postural instability
- SMART: Shuffling-Gait, Mask-like Face, Akinesia, Rigidity, Tremor
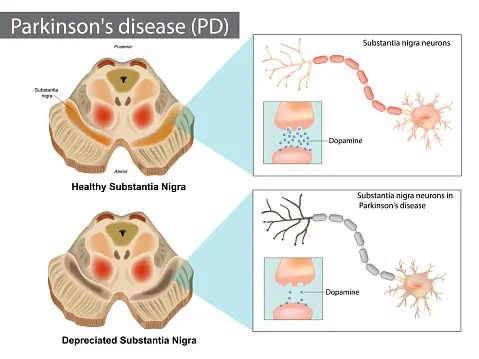
PD causes include genetic factors and environmental risks, leading to neuron breakdown in dopamine production areas of the brain. Key symptoms include bradykinesia, gait disorders, speech issues, and cognitive impairments.
Stage 5 Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
At this stage, patients struggle enormously with mobility and daily task performance. Symptoms include inability to rise from a chair unaided, hallucinations, and delusions, necessitating full-time care to prevent falls and assist with daily needs.
Evaluation and Treatment
Occupational therapy (OT) for Parkinson’s involves:
- Evaluation: Range of motion (ROM) tests, motor function assessments
- Treatment: Exercises for strength, coordination, and adaptive strategies using built-up or weighted utensils
- Adaptations: Environmental changes like using wheeled walkers and grab bars to aid mobility
Visit our full guide for detailed case examples and quizzes to enhance your understanding.
Stage 3 Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Increasing motor symptoms and balance issues define this stage. OT interventions focus on environmental modifications and adaptive techniques to assist in maintaining independence during everyday tasks.
Latest Trends in Managing PD
The Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT) BIG® and LOUD® programs offer advanced methods to improve mobility and communication in PD patients, showing significant results. Exercise-based regimens aim to recalibrate sensory perceptions and enhance neuroplasticity.
New Approaches
LSD microdosing is being explored for its potential benefits in managing Parkinson’s. By targeting serotonin receptors, LSD may influence dopamine biosynthesis, offering a novel approach to symptom management.
Want detailed practice tips to ace the NBCOT® exam? Join now for full access!
What are the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson's Disease?
The hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease include tremor, rigidity, and voluntary movement disorders such as akinesia and bradykinesia. These symptoms highlight dysfunction in both voluntary and involuntary movements.
How many stages are there in Parkinson's Disease and what are their characteristics?
Parkinson’s Disease is typically divided into five stages: Stage 1 with mild symptoms and minimal functional impairment, Stage 2 with early bilateral symptoms including facial masking and speech changes, Stage 3 with balance issues and slowness of movement, Stage 4 with severe symptoms requiring assistance for daily living activities, and Stage 5 with very advanced symptoms requiring wheelchair or bed confinement and round-the-clock care.
What are the signs of Parkinson's Disease according to the mnemonics TRAP and SMART?
The signs of Parkinson’s Disease can be memorized using the mnemonics TRAP and SMART. TRAP stands for Tremor, Rigidity, Akinesia, and Postural instability, while SMART stands for Shuffling-Gait, Mask-like Face, Akinesia, Rigidity, and Tremor.
What are the key features of Stage 5 Parkinson's Disease symptoms?
Stage 5 Parkinson’s Disease symptoms include severe mobility limitations, inability to rise from a chair unaided, hallucinations, and delusions. Patients require full-time care to assist with daily needs and to prevent falls.
What therapeutic approaches are recommended for Parkinson’s Disease, particularly Stage 3?
For Stage 3 Parkinson’s Disease, occupational therapy focuses on environmental modifications and adaptive techniques to maintain independence in daily life. Advanced approaches like the Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT) BIG® and LOUD® programs, along with exercise regimens, are used to improve mobility and communication. New approaches such as LSD microdosing are also being explored for managing symptoms.