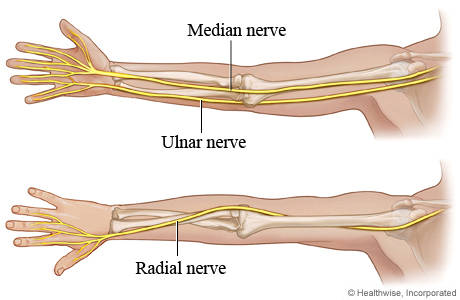
Welcome to our guide on neuropathies, crucial for NBCOT® exam prep. Here, we’ll explore the main peripheral nerves, common compressive neuropathies, and how these apply to real-world scenarios and exams.
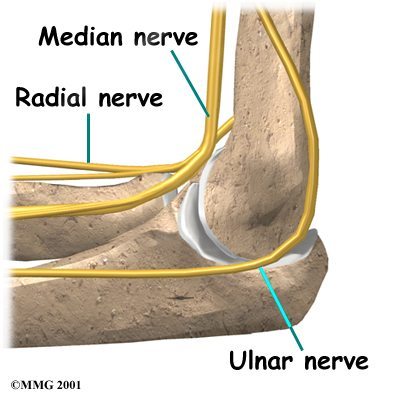
Radial Nerve Palsy: Causes and Symptoms
Radial nerve palsy can result from improper crutch use, fractures, and compression. It presents with the signature “wrist drop” and affects the ability to extend the wrist and fingers.
- Symptoms: Loss of movement, wrist drop, and numbness in hand.
- Action: Use wrist extension exercises to support recovery.
In our full guide, we compare radial tunnel syndrome and differentiate it from interosseous nerve syndromes (our exclusive walkthrough will be available for members!)
Wartenberg’s Sign in Ulnar Nerve Conditions
The Wartenberg sign highlights ulnar nerve issues. Notably, it manifests when the little finger abducts due to muscle weakness, indicating ulnar nerve compromise.
- Study Tip: Familiarize yourself with Froment’s sign alongside Wartenberg’s sign.
Explore exclusive quizzes on identifying these signs in our full guide.
Understanding Anterior Interosseous Nerve and Its Impact
The anterior interosseous nerve, a branch of the median nerve, crucial for hand pronation and flexion, does not affect sensation. Lesions here create difficulty in forming the OK sign.
- Key Learning: Distinguish between sensory and motor deficits for full comprehension.
Interactive case studies await you in the full content to practice differential diagnosis.
Ape Thumb Deformity: Recognizing the Pattern
The ape thumb deformity is seen with median nerve lesions, where thumb opposition becomes difficult, impacting grip and dexterity.
- Exam Strategy: Visual cues and mnemonic devices are invaluable for recall.
Unlock detailed illustrations and mnemonics with full access.
Complete Claw Hand: Examining Ulnar and Median Nerve Compression
Complete claw hand occurs with combined lesions of both the median and ulnar nerves, which result in the intrinsic minus position of the hand.
- Clinical Tip: MCP hyperextension and IP joint flexion are pivotal diagnosis hints.
Engage with our assessment tools in the members’ portal for active learning.
Radial Nerve Numbness and Damage Symptoms
Recognize symptoms of radial nerve damage, such as numbness, dorsal hand weakness, and a severe loss of functional wrist and finger extension.
- Investigate radial tunnel tests and treatment to broaden understanding.
For an interactive session on case assessments of radial nerve neuropathies, join our course today!
Want detailed practice tips to ace the NBCOT® exam? Join now for full access!
What are the common causes and symptoms of radial nerve palsy?
Radial nerve palsy often arises from improper crutch use, fractures, or compression. Key symptoms include wrist drop, loss of movement, and numbness in the hand. Wrist extension exercises can support recovery.
How is Wartenberg's sign related to ulnar nerve conditions?
Wartenberg’s sign indicates ulnar nerve issues, demonstrated by the abduction of the little finger due to muscle weakness. It’s essential to distinguish this from Froment’s sign for better diagnostic accuracy.
What impact does an anterior interosseous nerve lesion have?
Lesions in the anterior interosseous nerve, a branch of the median nerve, impair the ability to form an ‘OK’ sign, affecting hand pronation and flexion, but do not impact sensation.
How do median nerve lesions lead to the ape thumb deformity?
Median nerve lesions result in ape thumb deformity, where thumb opposition is difficult, affecting grip and dexterity. Visual cues and mnemonics are useful strategies for recognizing this pattern.
What are the diagnostic clues for complete claw hand due to nerve compression?
Complete claw hand, a result of median and ulnar nerve lesions, is identified by MCP hyperextension and IP joint flexion. Recognizing these signs is crucial for diagnosis.